Pressure Volume Loop Systole Diastole

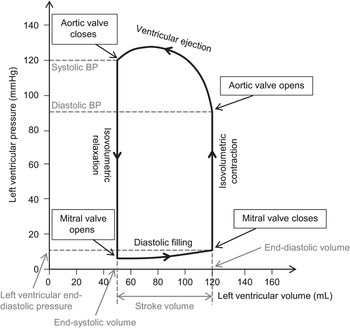
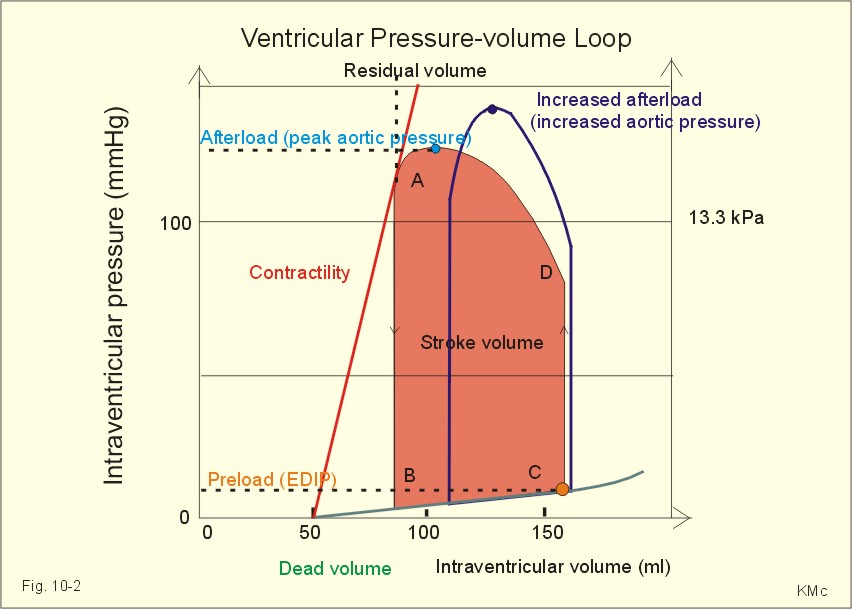
The preload or end diastolic volume is the load or volume right before systole at point c.
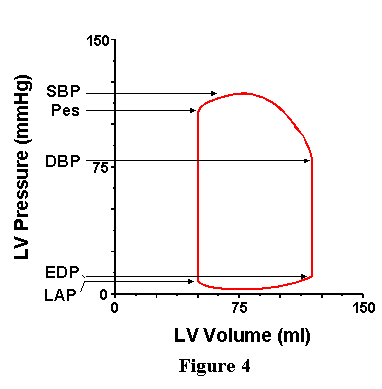
Pressure volume loop systole diastole. The afterload or end systolic volume is volume of the ventricles after systole and it is about 50 ml point a 14. End systolic end diastolic pulse pressure stroke volume and ejection fraction can be easily figured out using the pressure volume loop. Figure out how all of those physiology terms. Pressure volume loops are graphs where the pressure inside the left ventricle is on the y axis and the volume of the left ventricle is on the x axis.
It is about 130 ml. Volume plot pressure volume diagram a number of methods have been determined for measuring pv. Rishi is a pediatric infectious disease physician and works at khan academy. Ventricular filling phase a.
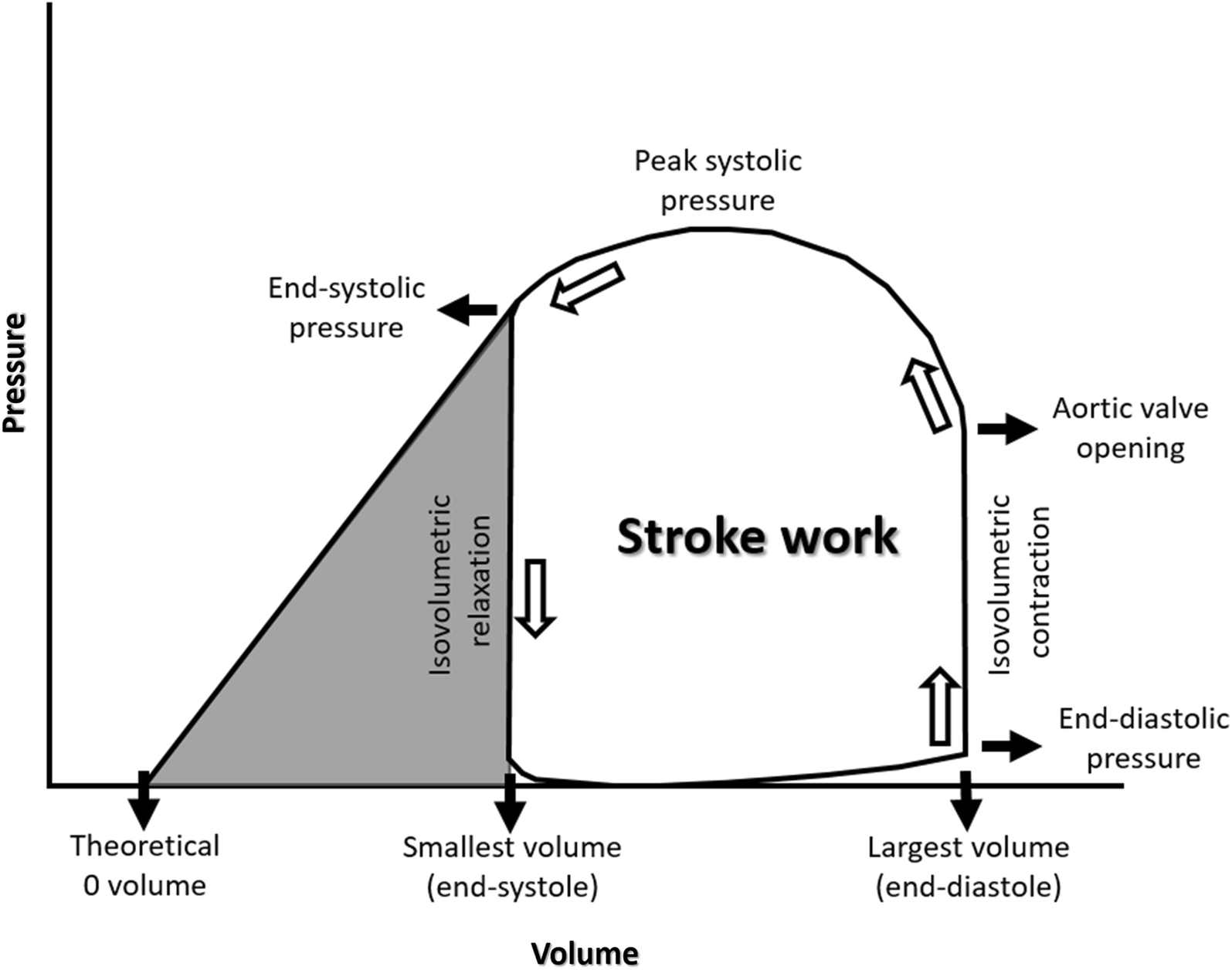
Systole and isovolumetric relaxation phase d. Diastole isovolumetric contraction phase b. To illustrate the pressure volume relationship for a single cardiac cycle the cycle can be divided into four basic phases. Systole ejection phase c.
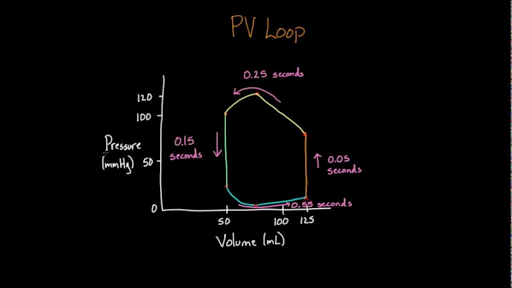
The pressure volume loop has four characteristic phases fig. This analysis can be applied to heat engines and pumps including the heart a considerable amount of information on cardiac performance can be determined from the pressure vs. Beginning at the bottom right corner of the loop an initial upstroke 1 2 represents the rapid increase in ventricular pressure with little volume change isovolumic contraction. Each loop represents one cardiac cycle including both ventricular systole and diastole or more simply one heartbeat.
Point 1 on the pv loop is the pressure and volume at the end of ventricular filling diastole and therefore represents the end diastolic pressure and end diastolic volume edv for the ventricle.